

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2023.12.08
2023.12.08Yes, it is possible to convert from multimode to single mode fiber by using a mode conditioning patch cable. This type of cable contains a small length of single mode fiber at the transmitting end and a small length of multimode fiber at the receiving end, which helps to minimize the modal dispersion that occurs when transitioning between the two fiber types. Additionally, a media converter can be used to convert the signal from multimode to single mode fiber.
Convert Multimode SFPs to Single-Mode and Save Money with Transponders
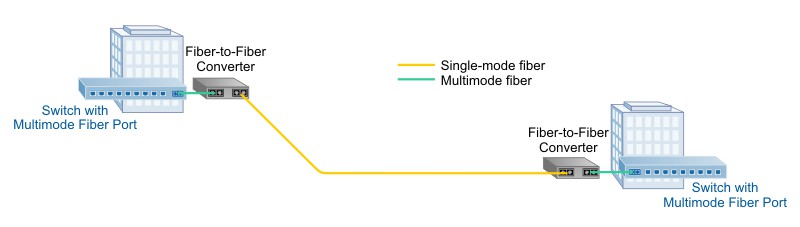
In this application example, multimode to single-mode fiber conversion is required for longer network distances. The fiber switches can be Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or any other network protocol. The fiber switches require the use of proprietary (name-brand switch manufacturer) single-mode SFPs that can be very expensive. Using third-party single-mode SFPs can void the manufacturer’s warranty and service contract.
Transponders are used to convert the 850nm multimode to 1310nm single-mode fiber. The transponders with multimode and single-mode SFPs can cost 50% less than buying proprietary single-mode SFPs and installing them in the switches. Since the transponders are external to the switches, they do not void the warranty or service contract from the switch manufacturer.

Single-mode Fiber (SMF)
Single-mode fiber (SMF) is a single strand of glass fiber that transmits data over long distances with a higher transmission speed that can emit only a single ray of light at any time. Single-mode fiber core is typically 8 to 9 microns, which is smaller than multimode fiber (MMF) and is used for longer-distance applications with up to 100 Gbps data rates. Single Mode fiber (SMF) cable uses laser light and is, therefore, more expensive than multimode fiber. Single-mode fiber (SMF) is used to connect devices over longer distances. The maximum distance for single-mode fiber is 140 kilometers.
Multimode Fiber (MMF)
As its name indicates, multimode optical fiber carries multiple light rays simultaneously at different speeds and reflection angles due to its larger core diameter. Multimode fiber core is typically 50 or 62.5 microns and is used in premises applications with up to 10 Gbps data rates. Multimode fiber (MMF) transmits data over shorter distances but provides high bandwidth at high speeds.
If you exceed the distance limit of multimode fiber, the data being transmitted may experience attenuation, or a loss of signal strength. This can result in errors in the transmitted data, which can lead to data corruption or loss. The distance limit for multimode fiber is determined by the quality of the fiber and the type of signal being transmitted. Generally, the longer the distance of the multimode fiber, the greater the attenuation.
Distance / Speed on Multimode Fiber
| Catalog | Type | Core | 1G | 10G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM1 | Multimode | 50 micron | 220 meters | 33 meters |
| OM2 | Multimode | 50 micron | 550 meters | 82 meters |
| OM3 | Multimode | 50 micron | 550 meters | 300 meters |
| OM4 | Multimode | 50 micron | 550 meters | 400 meters |
Multimode fiber (MMF) is cheaper than single-mode fiber (SMF) as it uses LED light, which is not powerful. Multimode fiber is used for short distances to connect devices in one particular building. The maximum distance for multimode fiber (MMF) is 2 km for 100Mbps applications.
There are several different types of multimode fiber available for high-speed network applications, and each with a different distance and speed capability. The table below shows the difference between the types of multimode cabling.
Multimode Fiber vs Single-mode fiber
Multimode fiber (MMF) and single-mode fiber (SMF) are types of fiber optic cabling types designed to transmit light signals over long distances. The main difference between multimode fiber (MMF) and single-mode fiber (SMF) is in the size of the fiber cores and the devices that connect to them. The core size determines the distance a signal can travel without signal distortion. Larger the core size the shorter the distance. That is the main reason multimode fiber is used for indoor applications.
| Fiber Optic Types | Core Size | Wavelength | Transmission Distance |
|---|---|---|---|
Multimode Fiber (MMF) | 50 or 62.5 microns | 850/1310nm | 2 kilometers |
Single-mode Fiber (SMF) | 8 to 9 microns | 1310/1550nm | 140 kilometers |
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
