

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2024.10.18
2024.10.18400G QSFP-DD optical transceivers come in various flavors: SR8, DR4, FR4, LR4, and more. QSFP-DD DR4 has a key advantage in that it can interoperate with 100G single lambda optics. The PMD in IEEE802.3bs Clause 124 defines a DR4 transmitting a 400Gb/s aggregated signal on 4 fibers (PSM4). These 4 separated independent lanes transport a 100Gb/s each in PAM4 signal format up to a distance of 500m with single mode fiber with KP4 FEC.
The 100G DR1 in IEEE802.3cd is referred to as 100G-single lambda, which runs at 100Gb/s in PAM4 on a single wavelength. The intended use for the DR1 is to interface with the 400G DR4.
400G DR4 transceivers typically come with MPO connectors but there are transceivers on the market now with SN connectors which are specially designed for breakout applications.
>>>You might be interested.What does 400G QSFP-DD Optical Module mean?
Benefits
This interoperability between 400G and 100G allows for greater flexibility for network upgrades. If you are upgrading your network from 100G to 400G, you need a cost-effective way to connect new equipment to what already exists in your data center. 400G DR4 optics offers you the ability to upgrade just one site with 400G host platforms and still connect it to existing 100G sites.
Connection Solutions
The 400G QSFP-DR4 optical module uses a 1310nm EML transmitter type, with signals modulated via PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation). It can transmit over single-mode fiber for distances up to 500 meters, suitable for short-distance 400G, 200G, and 100G optical interconnects. Below are two connection solutions for the 400G QSFP-DR4 optical module:
It can connect to the 100G QSFP28 DR optical module on the other end via an MPO-12 to 4*LC duplex breakout fiber patch cable.
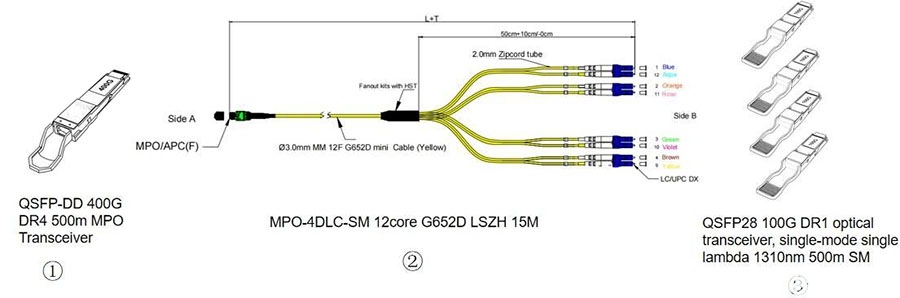
It can connect two 400G QSFP-DD DR4 optical modules within a data center using an MPO/MTP-8 single-mode fiber patch cable to achieve 400G transmission.

At the same time, with the mature development of silicon photonics technology, the 400G QSFP-DD DR4 silicon photonics module adopts a silicon photonics chip, effectively controlling costs and power consumption while enabling ultra-high-capacity data exchange. As large 400G data centers continue to grow, the demand for 400G QSFP-DD DR4 optical modules is steadily increasing.
Tips to keep in mind
In order to breakout one 400G-DR4 into four 100G-DR1, there are a few key things to keep in mind:
The 100G Ethernet lanes are independent and can be asynchronous to each other.
Each of the four lanes may not be active.
There are registers to check to make sure the transceiver DUT supports what the equipment wants to do and the equipment follows the compliance codes.
The most frequent mistake in operating the 1-λ transceivers is to have FEC on the host side.
In the extended ID field, A0(00).192 which is defined in SFF-8024, identifies the Extended Specification Compliance Code for the transceiver:
A0(0).0xC0=25h 100GBASE-DR1, CAUI-4 (no FEC)
A0(0).0xC0=26h 100GBASE-FR1, CAUI-4 (no FEC)
A0(0).0xC0=27h 100GBASE-LR1, CAUI-4 (no FEC)
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
