

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2024.01.18
2024.01.18SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, and QSFP28 are different fiber transceiver types on
the market. They are all hot-pluggable optical modules that are used to connect
network switches or other devices. Then, SFP vs. SFP+, SFP28 vs. SFP+, QSFP vs.
QSFP28, what are their differences? Can SFP28 transceiver plug into SFP+ slots?
And how to choose between these five form factors transceiver modules? All
explanations are here.
Pluggable Transceiver Optics are generally broken down into seven broad categories: SFP, SFP+, QSFP+, SFP28, QSFP28, QSFP-DD, and OSFP. These terms refer to the form factor and transmission data rate.
Table of Contents:
What is the SFP28 Transceiver?
What is a QSFP-DD Transceiver?
SFP vs. SFP+ vs. SFP28 vs. QSFP+ vs. QSFP28 vs. QSFP-DD vs. OSFP, What is the difference?
SFP stands for small form-factor pluggable. It is also known as a “mini-GBIC” (gigabit interface converter). An SFP transceiver is a tiny transceiver that links fiber optic cables to various networking devices such as switches, routers, network cards, and wireless access points. Multiple SFP transceivers are available, depending on data rate and application, including 155M SFP, 622M SFP, 1G SFP, 2.5G SFP, 2G/4G Fiber Chanel SFP, 3G SFP, and 6G SFP. They are used in fiber-optic Ethernet networks, particularly common in commercial networks. SFP transceivers are one of the most widely utilized fiber-optic networking equipment nowadays.
Compared to SFP transceivers, SFP+ transceivers are a more advanced version of the technology. SFP+ transceivers are most typically offered at 8Gbps, 10Gbps, or 16Gbps. They have the exact dimensions of SFPs, making it simple to integrate them into existing infrastructure. SFP+ transceiver is one of the most popular data center cabling applications.
Depending on the application, the SFP+ transceiver can be divided into five broad categories: Dual Fiber SFP+, BiDi SFP+, Copper SFP+, CWDM SFP+, and DWDM SFP+.
SFP28 stands for Small Form-Factor Pluggable 28. It is the third generation of SFP connection systems built for 25G throughput following the IEEE 802.3by specification (25GBASE-CR). The SFP28 is an improved version of the SFP+ designed for 25G signal transmission. The SFP28 has the typical form factor as the SFP+, but it offers 25Gbps electrical connections per channel. Compared with SFP+, SFP28 provides a much higher bandwidth capability.
Depending on the application, the SFP28 transceiver can be divided into six broad categories: Dual Fiber SFP28, BiDi SFP28, CWDM SFP28, DWDM SFP28, SFP28 DAC, and SFP28 AOC.
QSFP+, often known as QSFP, is an abbreviation for quad (4-channel) small form-factor pluggable. QSFP+ optics is yet another tiny, hot-pluggable transceiver used in data transmission. Compared to SFP+, QSFP+ supports 4x10G or 4x14G SFP+ data rates to enable increased bandwidth capabilities. It provides several data rate options for Ethernet, Fibre Channel, InfiniBand, and SONET/SDH technologies.
QSFP28 is an abbreviation for quad small form-factor pluggable 28. The QSFP28 transceiver is intended for use with 100 Gigabit Ethernet, EDR InfiniBand, or 32G Fibre Channel networks. The QSFP28 100G transceiver has four high-speed differential signal channels with data rates ranging from 25 Gbps to 40 Gbps. In the 100G optics market, QSFP28 transceivers are more popular than CFP, CFP2, and CFP4 form factors.
Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double Density (QSFP-DD) is also known as QSFP56-DD. The QSFP-DD transceiver is a new optical module comparable to the current QSFP but adds an extra row of contacts for an eight-lane electrical interface. All QSFP-DD-based transceivers from 40G to 200G are backward compatible with QSFP+. In a single rack unit (RU), QSFP-DD can support 36 400GbE ports, with a total bandwidth of nearly 14Tb/s.
The OSFP acronym stands for Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable. The OSFP MSA designed it. Google launched the OSFP MSA group, which Arista Networks heads. OSFP is a revolutionary pluggable form factor that offers eight high-speed electrical channels at 400 Gbps (8x50G or 4x100G). However, it supports 32 OSFP ports per 1U front panel and 14.4 Tbps per 1U swap slot. OSFP optics with improved signal integrity and thermal performance are being developed to suit the next generation of 800G optics. The OSFP may also be used with 100G QSFP optics.
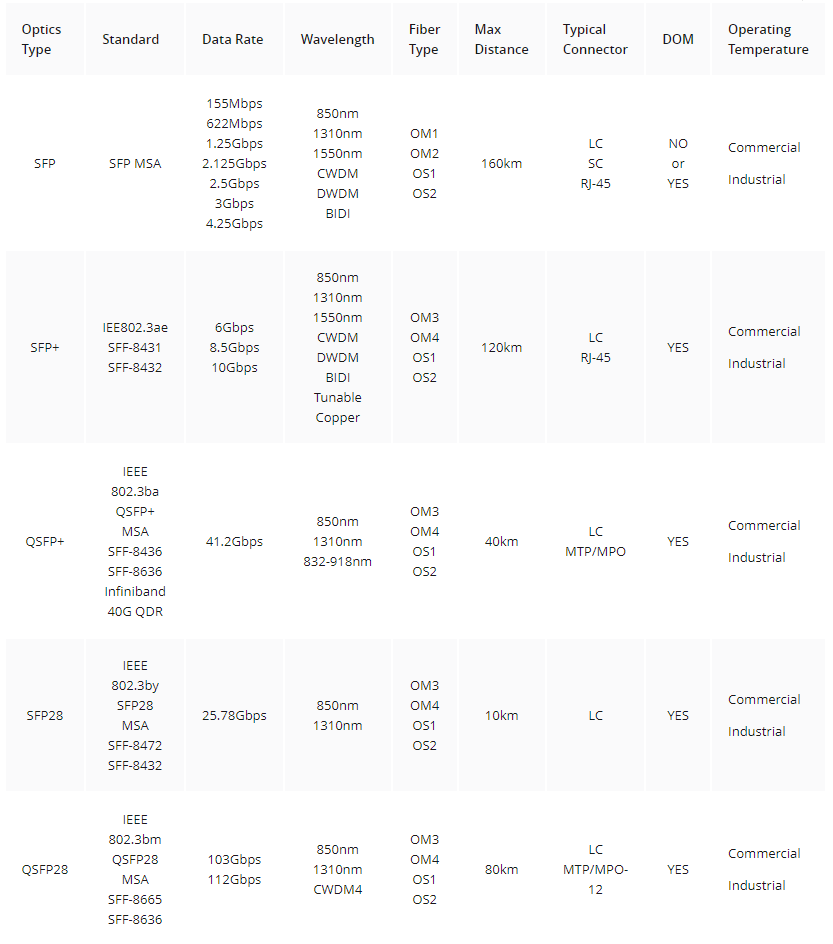
It's clear that the main driving force behind the evolution of optical transceivers is the need to achieve higher bandwidth rates with smaller form factors. In modern, dense networks, small form factors are a constant necessity. SFP vs SFP+ vs SFP28 vs QSFP+ vs QSFP28, after a clear understanding of them, you also have to consider your network traffic, transmission distance, and future-proof networking requirements to ensure the right selection.
Read More
What is 400G QSFP-DD optical module?
How to choose an appropriate optical fiber jumper for the QSFP-DD 800G optical module
Why Use QSFP 40G UNIV Transceiver for 40G
What is the standard for QSFP 100G
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
