

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2023.12.04
2023.12.04What is QSFP?
QSFP abbreviation stands for Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable.
QSFP is available for use in both single-mode and multimode and can to support 4 independent channels that can individually transmit at up to 1.25 Gbps per channel for a total speed of above 4 Gbps.
QSFP vs QSFP+
What is QSFP+? QSFP+ stands for Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus,which is an upgraded version of QSFP designed to accommodate higher data transmission speeds. The QSFP+ speed is characterized by its ability to handle four 10 Gbit/s channels, thereby enabling it to carry 10-Gigabit Ethernet, 10G Fiber Channel, or InfiniBand. This allows for the use of 4x10G cables and enables QSFP+ to break out into 4x10G or 1x40G connections. QSFP+ modules can be applied to connecting switches, Host Bus Adapters (HBAs), data centers, high-performance computing (HPC), and storage systems.
QSFP+ vs QSFP28
What Is QSFP 28?
QSFP 28 stands for Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable 28, which is an upgraded version of QSFP+. The “28” shows that each lane can carry up to 28G data rate. QSFP 28 is designed for 100G applications as SFP28 can do 4x25G breakout connection, 2x50G breakout, or 1x100G depending on the transceiver. Accordingly, it is possible for a QSFP 28 to be connected with a 40G QSFP+ transceiver.
The QSFP 28 comes in many different features. Let’s delve in deeper:
4 Electrical Lanes: With the speed of transmitting data at 28 Gbps, the configuration allows QSFP 28 to achieve a total potential data transfer rate of up to 112 Gbps.
Hot-Swappable Design: Allows replacement without network shutdown, valuable for mission-critical applications.
Advanced IC Technology: Utilizes integrated circuits with digital signal processing, equalization, and clock data recovery for high-speed data transfer.
Digital Signal Processing (DSP): Compensates for signal distortion caused by the transmission medium, enhancing signal-to-noise ratio and ensuring reliable data transmission.
Equalization: Corrects signal distortion from the transmission channel, maintaining signal integrity and reducing errors.
Clock Data Recovery (CDR): Extracts the clock signal accurately from incoming data, enabling synchronization for proper decoding and error correction.
Different QSFP 28 Modules
QSFP 28 modules come in different configurations, each designed to meet specific data transmission requirements. The different types are distinguished by the type of transmission media, transmission rate, transmission distance, and power consumption. Every QSFP 28 module includes one or more QSFP 28 transceivers, ports, and connectors. These components determine the configuration and capabilities of the module. A few common QSFP 28 modules include:
QSFP28 SR4: Designed for short-range transmission but with a low wavelength of 850 nm, this module uses multi-mode fiber (MMF) to support a maximum transmission distance of 100 meters.
QSFP28 LR4: Using duplex single-mode fiber, this module prioritizes long-range transmissions with a maximum transmission distance of 10 kilometers.
QSFP28 PSM4: With parallel single-mode fiber, it uses four pairs of single-mode fibers to transmit data. It operates at a wavelength of 1310 nm.
QSFP28 CWDM4: To operate at 4 different wavelengths, CWDM4 uses a single pair of single-mode fibers to transmit data.
Each of these modules comprises one or more QSFP28 transceivers, ports, and connectors, which collectively determine the module’s configuration and capabilities. The various configurations of the QSFP28 ports in these modules allow for a flexible and robust data communication infrastructure.
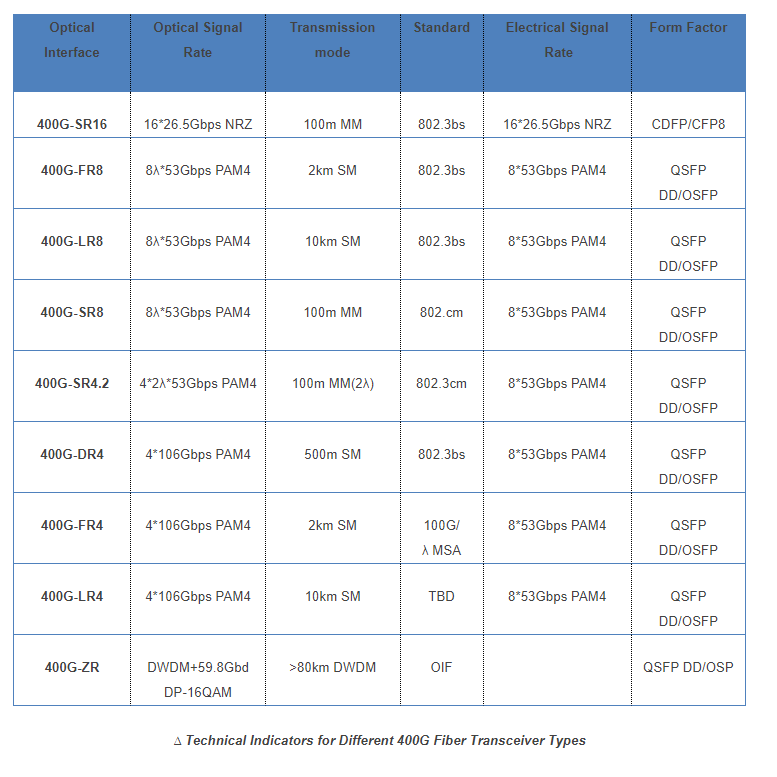
QSFP-DD VS. QSFP28
The primary differences between QSFP-DD and QSFP28 are centered around their structure, bandwidth, and backward compatibility. While both have similar dimensions, QSFP-DD is equipped with an 8-lane electrical interface, doubling the ASIC ports to support existing interfaces like CAUI-4. This increases the module's bandwidth capability to 400Gbps, compared to QSFP28's 100Gbps.
Furthermore, QSFP-DD's mechanical interface on the host board is slightly deeper to accommodate the extra row of contacts. This design makes QSFP-DD backward compatible with previous QSFP system transceiver modules, aiding in reducing network upgrade costs while supporting higher bandwidths1.
Related Articles
How does the QSFP DD 400G LR4 optical transceiver accomplish a data rate of 400Gbps
How does QSFP DD work
How far can the QSFP DD 400G LR4 optical transceiver reach
How many lanes are in QSFP DD
What is the difference between QSFP DD and QSFP56
What is the difference between QSFP DD and QSFP DD800
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
