

 Industry Dynamic +
Industry Dynamic +  2023.10.28
2023.10.28This article contains:
Difference between QSFP-DD and QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56
Difference between QSFP-DD and OSFP/CFP8/COBO
QSFP-DD is highly sought after by vendors as the smallest-sized package for 400G optics, offering high port density and backward compatibility with QSFP+/QSFP28 packages. Nowadays, many vendors have launched 400G QSFP-DD products, such as 400G QSFP-DD optical modules and 400G QSFP-DD DAC/AOC. So how much do you know about QSFP-DD packaging? In this article, we will bring you to know the QSFP-DD package again, and understand the difference between it and QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 and OSFP/CFP8/COBO packages.

QSFP-DD Package Overview
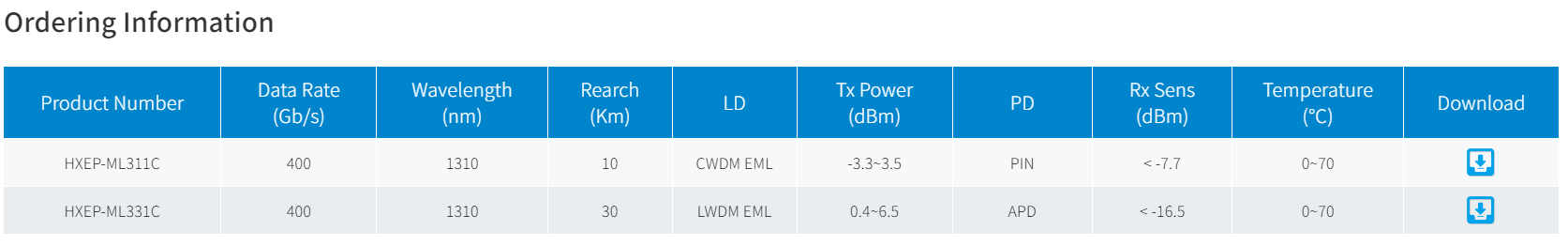
QSFP-DD (also known as QSFP56-DD) is a dual-density, four-channel, compact pluggable package that is a new type of high-speed pluggable module package that complies with the IEEE802.3bs and QSFP-DD MSA standards. The electrical interface of this package has 8 channels, and the data rate of each channel can reach 25Gb/s through NRZ modulation technology to achieve 200G network transmission, and the data rate of each channel can reach 50Gb/s through PAM4 modulation technology to achieve 400G network transmission, which is suitable for high-performance computing data centre and cloud network.
More about "Types of 400G QSFP-DD transceivers"
The advantages of QSFP-DD are shown in the following aspects:
Backward compatibility with QSFP packages such as QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56;
Adoption of 2×1 stacked integrated cages and connectors, which can support single-height and dual-height cage connector systems;
Using SMT connectors and 1xN cages, the cage design and optical module enclosure optimisation enables a thermal capacitance of at least 12 watts per module. The higher heat capacity reduces the optical module's requirement for heat dissipation functions, thus reducing some unnecessary costs.
When designing the QSFP-DD the MSA working group took full consideration of user flexibility and adopted an ASIC design that supports multiple interface rates and is backward compatible (QSFP+/QSFP28 compatible), thus reducing port costs and equipment deployment costs.
All in all, QSFP-DD is a high-speed, small, pluggable and low-power package, which will become one of the mainstream packages for 400G. So what is the difference between QSFP-DD and the previous QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56? And how does it differ from other 400G packages such as OSFP/CFP8/COBO?
Difference between QSFP-DD and QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56
Although QSFP-DD and QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 belong to the same QSFP package and have the same dimensions, there are still some differences between them.
Structure
In terms of structure, QSFP-DD and QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 have some differences in the depth of the mechanical interface on the motherboard, the number of channels on the electrical interface, and the number of integrated circuits. The details are as follows:
Motherboard Mechanical Interface Depth - When the MSA team members designed the QSFP-DD, in order for the QSFP-DD to have the same port density as the QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 and to be able to accommodate the extra row of contacts, the mechanical interfaces on the motherboard are slightly deeper than the QSFP+/QSFP28/ QSFP56's slightly deeper.
Number of Electrical Interfaces - As seen above, the QSFP-DD package is equipped with 8 channels of electrical interfaces, which is double the number of electrical interfaces compared to the 4-channel electrical interfaces of the QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 packages, thanks to the extra row of contacts in the QSFP-DD package.
Number of Integrated Circuits - Although the QSFP-DD is the same size as the QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56, because the QSFP-DD has an 8-channel electrical interface, the number of integrated circuits (i.e., ASICs) and density are increased by one compared to the 4-channel electrical interface of the QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56. ASICs) and density are doubled compared to 4-channel electrical interfaces for QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56.
Bandwidth & Applications
As you can see from the above, the maximum bandwidth of QSFP-DD can reach 400Gbps, while the maximum bandwidth of QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 can only reach 40Gbps/100Gbps/200Gbps respectively, which is much higher than that of QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56. Because of this, QSFP-DD is usually used as 400G optical module and 400G high-speed cable (i.e., DAC and AOC) package for 400G data centre interconnect, to solve the problem of high-speed migration of massive data between data centres; while QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 are used for 40G/100G/200G optical module and high-speed cable package respectively, for 40G/100G/200G network interconnections.
Compatibility
QSFP-DD has backward compatibility, supporting existing QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 packaged modules or connectors to be inserted into QSFP-DD ports; however, QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 ports do not support the use of modules or connectors in QSFP-DD packages.
In short, the QSFP-DD package has been technologically upgraded based on the continuation of the advantages of previous packages, which increases the bandwidth and better meets the large bandwidth network applications. At the same time, backward compatibility can effectively reduce the replacement of equipment, saving network upgrade costs.
Difference between QSFP-DD and OSFP/CFP8/COBO
Although QSFP-DD (QSFP56-DD) and OSFP/CFP8/COBO are both 400G packages, there are certain advantages and disadvantages of these four 400G packages, as follows:
QSFP-DD - As can be seen above, this package is compatible with existing QSFP+/QSFP28, has a small size, and is easy to maintain.
OSFP - This package also uses an 8-channel electrical interface, with a data rate of 50Gbps per channel, and comes with a heat sink, which can largely improve heat dissipation; however, the new interface standard, which is incompatible with the existing optical-electrical interfaces, is slightly larger than the QSFP-DD, requires a larger area of the printed circuit board (PCB) ) with high power consumption.
CFP8 - equivalent to a high-speed evolution version of CFP4, the electrical interface of the channel can be 8 channels or 16 channels (16 channels mostly), can be quickly put into the market, suitable for telecom backhaul; but the cost is higher, size and power consumption.
COBO - with the above package is different, it will be placed in the PCB optical module, not limited to the front panel interface density, and can use the motherboard heat dissipation, heat dissipation is good, the size is small; but does not support hot plug, the later maintenance is more difficult.
Because of this, QSFP-DD and OSFP have become the packaging technology of choice for most suppliers. Only, QSFP-DD is more suitable for data centre applications, while OSFP packaging is more suitable for telecom applications.
Walsun can provide customers with customised design and services to meet the needs of customers' special products. If you need to buy related products or consult more related issues, you can leave a message in the "contact us" to send your needs, we will respond to your information within 48 hours.
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
