

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2024.08.27
2024.08.27Optical module is the optoelectronic device that realizes photoelectric and photoelectric conversion in optical communication, and is the core part of optical communication industry. The form factors of fiber transceivers have changed from GBIC packaging before to smaller SFP packaging and then to the current 800G QSFP-DD and 800G OSFP packaging. The overall development of 800G transceiver toward higher speed, miniaturization, hot-swappable direction. The main application scenarios include Ethernet, CWDM/DWDM, connectors, Fiber Channel, wired access and wireless access, and the sub-scenarios cover the data communication market and the telecom market.
Overview of 800G Transceivers
800G optical transceivers are high-speed optical transmission technologies designed to support data rates of 800Gbps. They are widely used in data centers, cloud computing, and 5G communications to handle massive data loads and meet the needs for high bandwidth and fast data transmission needs. QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable Double Density) and the OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable) are two packages of 800G optical modules, both supporting 8-channel transmission, which are the two mainstream package forms of 800G transceivers at present.
Key Differences Between QSFP-DD and OSFP
There are similarities and differences between QSFP-DD and OSFP. The following will introduce their differences in detail from the aspects of form factor, power consumption, heat dissipation, compatibility and application.
800G Transceiver Form Factors Advantages
800G QSFP-DD Form Factor:
Dual-density four-channel small pluggable high-speed module. QSFP-DD is currently the preferred package for 800G optical modules, enabling data centers to efficiently grow and scale cloud capacity as needed. The QSFP-DD module uses 8-channel electrical interfaces with rates up to 25Gb/s (NRZ modulation) or 50Gb/s (PAM4 modulation) per channel, providing solutions up to 200Gb/s or 400Gb/s aggregation.
The Advantages of 800G QSFP-DD:
1. With backward compatibility, compatible with QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP56 QSFP package.
2. Adopt 2×1 stacked integrated cage and connector, can support single height and double height cage connector system.
3. With SMT connectors and 1xN cages, cage design and optical module housing optimization enable a heat capacity of at least 12 watts per module. The higher heat capacity can reduce the heat dissipation function requirements of the optical module, thus reducing some unnecessary costs.
4. In the design of QSFP-DD, the MSA working group fully considered the flexibility of user use, adopted the ASIC design, supported a variety of interface rates, and could be backward compatible (compatible with QSFP+/QSFP28), thus reducing port costs and device deployment costs.
800G OSFP Form Factor:
The OSFP is a new type of optical module, much smaller than the CFP8 but slightly larger than the QSFP-DD, with eight high-speed electrical channels that still support 32 OSFP ports on each 1U front panel. With an integrated heat sink, it can greatly improve heat dissipation performance.
The Advantages of 800G OSFP:
1. The OSFP module is designed as an 8-channel (Octal, or 8 lane), directly supporting a total throughput of up to 800G, enabling higher bandwidth density.
2. Because the OSFP package supports more channels and higher data transfer rates, it can provide higher performance and longer transmission distances.
3. OSFP module has excellent thermal design and can handle higher power consumption.
4. OSFP is designed to support higher rates in the future. Due to the larger size of the OSFP module, it has the potential to support higher power consumption and thus higher rates, such as 1.6T or higher.
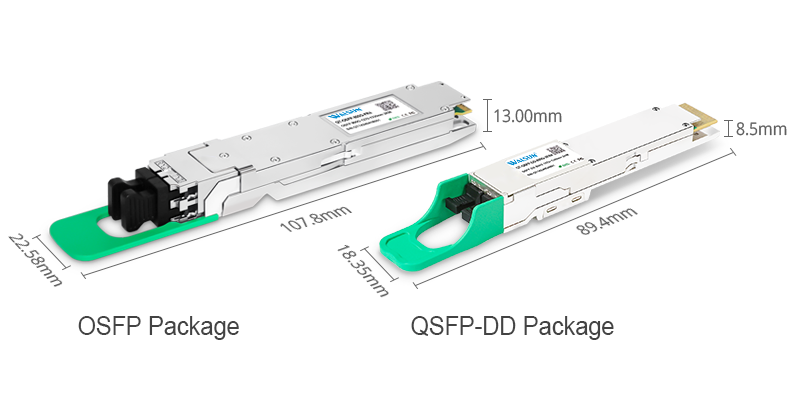
800G Transceiver Form Factors Parameter Comparison:
QSFP-DD | OSFP | |
|---|---|---|
Size(length*width*height) | 89.4mm*18.35mm*8.5mm | 107.8mm*22.58mm*13.0mm |
Electrical Lanes | 8 | 8 |
Single Lane Rate | 25Gbps/50Gbps/100Gbps | 25Gbps/50Gbps/100Gbps |
Total Max Data Rate | 200G/400G/800G | 200G/400G/800G |
Modulation | NRZ/PAM4 | NRZ/PAM4 |
Backward Compatibility with QSFP+/QSFP28 | Yes | No |
Port density in 1U | 36 | 36 |
Bandwidth in 1U | 14.4Tb/s | 14.4Tb/s |
Power consumption Upper Threshold | 12W | 15W |
Products | Transceiver Modules; DAC & AOC cables | Transceiver Modules; DAC & AOC cables |
How to Choose 800G Optical Transceivers?
Choosing the right 800G optical transceivers for your network requires careful consideration of several key factors. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
1. Network Requirements
Data Rate and Bandwidth: Ensure that the 800G transceiver supports the data rate required by your network. 800G transceivers are designed for high-bandwidth applications, such as data centers and high-performance computing (HPC) environments.
Transmission Distance: Consider the distance over which data needs to be transmitted. Different 800G transceivers are optimized for varying distances, from short-reach (up to 100 meters) to long-haul (up to 40 kilometers or more) applications.
Interface Type: Determine the type of interface that matches your existing infrastructure. Common interfaces include OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable) and QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density).
2. Application Scenarios
Data Center Interconnects: For connecting different data centers over longer distances, consider transceivers that support coherent technology, which can provide high performance over extended ranges.
Intra-Data Center Connections: For connections within a data center, consider short-reach transceivers that are optimized for high density and low power consumption.
Cloud and Hyperscale Networks: Hyperscale data centers and cloud providers require transceivers that can handle large volumes of data with low latency. Transceivers with advanced modulation formats like PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) are suitable for these environments.
3. Form Factor and Compatibility
Form Factor: Choose a transceiver with a form factor that is compatible with your equipment. OSFP and QSFP-DD are common form factors for 800G transceivers. Ensure that the transceiver fits into your existing or planned equipment.
Backward Compatibility: If you have existing infrastructure with 400G or lower capacity, consider whether the 800G transceiver offers backward compatibility or if adapters are needed.
4. Power Consumption and Thermal Management
Power Efficiency: Evaluate the power consumption of the transceiver, especially in large deployments. More power-efficient transceivers can reduce operational costs and heat generation.
Thermal Management: Consider the thermal design and cooling requirements of the transceiver. Efficient thermal management is critical for maintaining performance and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
5. Optical Modulation Technology
Modulation Format: Look for transceivers that use advanced modulation techniques such as PAM4 or coherent optics, which enable higher data rates and more efficient use of bandwidth.
Forward Error Correction (FEC): Ensure the transceiver supports FEC, which is essential for maintaining data integrity at higher speeds.
6. Cost Considerations
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider both the upfront cost of the transceiver and the long-term operational costs, including power consumption, cooling, and potential future upgrades.
Scalability: Evaluate whether the transceiver solution allows for future scaling, particularly as data demands grow. Investing in a scalable solution can reduce the need for frequent upgrades.
7. Vendor Support and Reliability
Quality and Reliability: Choose transceivers from reputable vendors that have a track record of quality and reliability. Look for products that meet industry standards and have undergone rigorous testing.
Vendor Support: Ensure that the vendor provides strong technical support and warranty options. This is especially important for high-speed, critical network components.
8. Future-Proofing
Network Evolution: Consider how the transceiver will fit into your network’s future evolution. 800G is at the forefront of optical communication technology, so ensuring compatibility with future standards and technologies is crucial.
Ecosystem Compatibility: Ensure the transceiver is compatible with other network components, such as switches, routers, and monitoring tools, to create a cohesive and future-proof network environment.
9. Latency and Performance Metrics
Low Latency: For applications like high-frequency trading or real-time data processing, low latency is critical. Ensure that the transceiver you choose has minimal latency to meet the demands of these time-sensitive applications.
Performance Benchmarks: Review the performance benchmarks of the transceivers, such as bit error rate (BER) and signal integrity. High-performance transceivers should maintain low BER even at maximum data rates and distances.
10. Optical Fiber Type
Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode: Determine whether your network uses single-mode (SMF) or multi-mode fiber (MMF). 800G transceivers are typically optimized for single-mode fiber due to the higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances it supports. However, ensure compatibility with your existing fiber infrastructure.
Fiber Count: Some 800G transceivers, like those using parallel optics, may require multiple fiber strands (e.g., 8 or 16 fibers). Ensure your network cabling can accommodate the fiber count required by the transceiver.
11. Deployment Environment
Indoor vs. Outdoor: Consider the deployment environment. For outdoor deployments, choose transceivers that are ruggedized or rated for outdoor use, with resistance to temperature fluctuations, moisture, and dust.
Edge vs. Core Network: In edge computing environments, you may require transceivers with lower power consumption and smaller form factors. For core networks, prioritize transceivers that support high-capacity and long-distance transmission.
12. Security Features
Data Encryption: In sensitive environments, look for transceivers that support data encryption to protect data in transit from unauthorized access or interception.
Firmware Security: Ensure that the transceiver's firmware is secure and can be updated to patch vulnerabilities. This is especially important as network components are often targets for cyber threats.
13. Management and Monitoring Capabilities
Diagnostics: Choose transceivers with built-in diagnostics and monitoring features such as Digital Diagnostics Monitoring (DDM) or Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM). These tools can help monitor parameters like temperature, voltage, and signal strength, enabling proactive maintenance.
Network Management Software: Ensure the transceiver is compatible with your network management software, allowing for seamless integration into your existing monitoring and management systems.
14. Standards and Compliance
Industry Standards: Verify that the transceiver complies with industry standards such as IEEE, ITU-T, and MSA (Multi-Source Agreement). Compliance with these standards ensures interoperability and reliability.
Environmental Compliance: Check for compliance with environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) to ensure that the transceiver meets environmental safety standards.
15. Testing and Validation
Compatibility Testing: Before full-scale deployment, conduct thorough compatibility testing with your existing network infrastructure. This includes testing the transceiver with switches, routers, and other network devices to ensure seamless integration.
Performance Testing: Perform performance tests under various conditions to ensure that the transceiver meets the required specifications in terms of data rate, latency, and error rates.
16. Vendor Selection and Supply Chain
Reliable Vendors: Choose transceivers from vendors with a proven track record of reliability and customer support. Research vendor reviews, case studies, and customer feedback to assess their reputation.
Supply Chain Stability: Consider the stability of the vendor's supply chain, especially in the context of global disruptions. Ensure that the vendor can deliver the transceivers on time and provide ongoing support for replacements and upgrades.
17. Customization Options
Custom Configurations: Some vendors offer customization options for 800G transceivers, such as specific wavelength configurations or tailored firmware settings. If your network has unique requirements, inquire about custom solutions.
Future Upgradability: Consider whether the transceiver supports future upgrades, such as firmware updates or modular add-ons, to extend its lifecycle and maintain compatibility with evolving network standards.
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
